- On this page
- What is digital identity management?
- Why is digital identity management important?
- Types of digital identities
- What is identity and access management?
- Today’s challenges of digital identity management
- Why – or not – outsource digital identity management
- Operating models for digital identity systems
- Embracing digital transformation with the right amount of support
In the era of digital transformation, digital identity management emerges as a key enabler for organizations seeking to enhance cybersecurity, strengthen customer trust, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Delve into the transformative power of digital identity management. Learn what it’s all about and why organizations cannot afford to ignore the topic. Explore its challenges and – finally – find out whether outsourcing might be an option for your organization by comparing risks and benefits.
What is digital identity management?
Digital identity management refers to the processes and technologies used to manage and secure information about the identity of individuals or entities within a digital system. This includes the creation, maintenance, and use of digital identities. Identity management encompasses a variety of components and practices, including authentication, authorization, and identity governance.
Why is digital identity management important?
Today, data is the most valuable commodity in the world. This is reflected by the ever-increasing number of cyberattacks.
According to the Swiss Federal Statistical Office, cybercrime in Switzerland increased by 31% in 2023 to 43’839 criminal acts. This was in particular due to phishing attacks (+69.8%) and the misuse of online payment systems and identities (+66.1%).

However, in times where digital interactions are everywhere, users must be able to trust that their identities and personal information are protected. Effective digital identity management provides this assurance by verifying that users are who they claim to be through strong authentication methods.
Furthermore, digital identity management plays a vital role in protecting organizations against breaches. By implementing stringent access controls and continuously monitoring identity activities, organizations can mitigate the risk of cyberattacks and data leaks. This not only protects the organization's assets but also upholds its reputation and trustworthiness.
In addition to user trust and security, regulatory compliance has become a mandatory aspect of identity management. Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and the Swiss Federal Act on Data Protection (FADP) impose strict requirements on how personal and sensitive information is managed. Adhering to these regulations is essential for legal compliance and avoiding significant penalties.
Thus, identity management is indispensable for maintaining security, ensuring user trust, and meeting regulatory standards in today's digital landscape.
Types of digital identities
A digital identity is the information and data that identifies an individual in the digital world. It consists of a set of attributes and credentials, such as name, date of birth, e-mail address, and biometrics, as well as certificates, passwords, or other cryptographic keys. Several types of digital identities coexist.
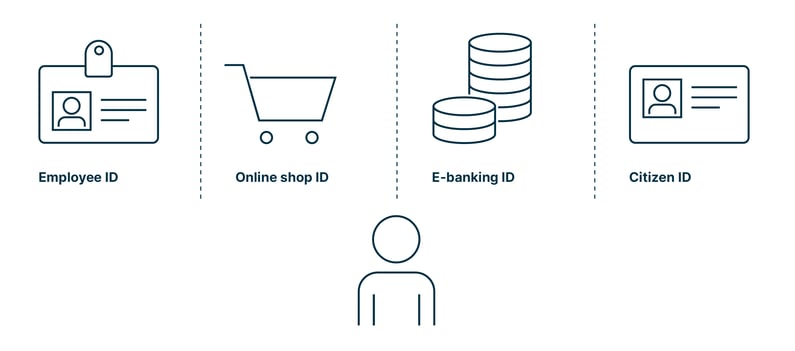
An employee ID allows the workforce of a company to access the internal network and enables organizations to manage permissions, monitor performance, and ensure compliance by identifying policy violations and risky access.
A consumer ID provides online shoppers with increased security while allowing providers to gather insights into user preferences and demographics, balancing security with a pleasant user experience.
A special kind of consumer ID is an e-banking ID, for example. In this case the security requirements are much higher. An e-banking ID can be used to access online banking services, view account information, and make transactions. At the same time providers – i.e., financial institutions – must gather a different kind of metrics, namely behavioral data, among other reasons to ensure a higher security standard.
Lastly, a citizen ID offers secure 24/7 access to government services online, encouraging digital use and reducing the need for office visits by ensuring privacy.
What is identity and access management?
Definition
Identity and access management (IAM) is a framework of policies and technologies ensuring the right individuals access the appropriate resources at the right times for the right reasons. It involves managing user identities and their permissions across systems, enhancing security and compliance.
There are several flavors of IAM, depending on the types of identities managed, but all of them are to some degree based on the following key concepts:
- Identification: Uniquely identifying users or entities
- Authentication: Verifying the identity of users through credentials or other means
- Authorization: Granting appropriate access rights based on user roles and permissions
- Accounting (or auditing): Logging and monitoring user activities for security and compliance purposes
- Life cycle management: Managing user identities throughout their life cycle, from creation to deletion or deactivation
- Integration and federation: Connecting IAM systems with other applications and supporting federated identity management
Various use cases – How EIAM, CIAM, and DIM differ from each other
 Enterprise IAM (EIAM) primarily focuses on managing and securing workforce digital identities within an organization, controlling access to resources based on roles, policies, and user attributes. It streamlines authentication, authorization, and user management processes for employee IDs.
Enterprise IAM (EIAM) primarily focuses on managing and securing workforce digital identities within an organization, controlling access to resources based on roles, policies, and user attributes. It streamlines authentication, authorization, and user management processes for employee IDs.
Customer identity and access management (CIAM) refers to the authentication and authorization of customer identities. CIAM plays an important role in protecting individuals from cyberthreats and focuses on security and integration to offer the best consumer experience possible.
Decentralized identity management (DIM), aka Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), distributes the control of identity management, giving full ownership of their identity data back to the user. DIM often involves technologies like blockchain. While this model enhances privacy and reduces the risk of centralized data breaches, it can be more complex to manage.
The next level of IAM: identity fabrics
Identity fabrics is a cutting-edge concept and methodology revolutionizing IAM. Functioning as a high-level architectural framework within IAM, it takes a centralized approach to deliver a comprehensive overview of all users and their access privileges. This unified perspective – as opposed to a silo approach – simplifies identity management and bolsters identity security by minimizing the potential for unauthorized access. Essentially, identity fabrics enable the strategic design of logical IAM infrastructures for enhanced efficiency and security.

Today’s challenges of digital identity management
Since digital identity management (IDM) is at the core of corporate activities, the challenges that come with it can affect multiple levels of operation, such as resources, technology, and processes. This means that it‘s incredibly important to understand these challenges and know how to deal with them.
Below, we will shed some light on the main challenges of IDM:
- resource shortages
- the complexity of managing systems and identities
- the need for rapid adaptation
- changing business requirements
- legal requirements and compliance

Resource shortages

When it comes to digital identity management, two types of resources can lead to problems if there is a shortage of them:
Firstly, human resources are an issue, as securely managing digital identities requires a broad range of qualified professionals which are hard to find: from IT administrators, application owners, security analysts, and compliance and data protection officers to cloud experts.
Secondly, financial resources play a key role: Smaller companies or those with limited IT budgets may struggle to allocate sufficient funds for hiring, training, and retaining IAM professionals or investing in necessary technologies.
Complexity of managing systems and identities

The complexity of digital identity management consists of several interrelated factors further emphasizing the need for highly skilled employees:
- Diverse systems and applications
Identity management needs to be integrated across a variety of systems, applications, and platforms, each with its own requirements and protocols.
- Authentication mechanisms
Implementing and managing various authentication methods, such as passwords, biometrics, and MFA, requires sophisticated technology and coordination. - Authorization and access control
Defining and enforcing granular access control policies, such as RBAC and attribute-based access control (ABAC), necessitates detailed planning and constant updates. - User life cycle management
From onboarding and provisioning to de-provisioning and offboarding – managing the entire life cycle of user identities requires streamlined processes and automation to handle changes efficiently. - Security and threat management
Protecting against a wide range of security threats, such as phishing, brute force attacks, and insider threats, requires advanced security measures and continuous vigilance. - Scalability
Ensuring that the identity management system can scale to accommodate growth, additional users, and increased data without compromising performance or security adds another layer of complexity. - Interoperability
Achieving interoperability between different identity management solutions and standards (e.g., SAML, OAuth, OpenID Connect) involves careful planning and implementation.
Need for rapid adaptation

In the ever-evolving digital landscape, rapid adaptation is required on multiple levels:
- Security threats
With new technologies and vulnerabilities, new attack vectors emerge. Quickly implementing updated security measures helps organizations stay ahead of these threats. - Incident response
In the event of a security breach or incident, rapid adaptation of identity management practices is crucial to mitigate the impact, secure systems, and prevent future incidents. - Regulatory compliance
Regulations and compliance standards are frequently updated to address new security concerns and protect user data. Companies must adapt quickly to meet these evolving requirements and avoid legal penalties. - User expectations
As users become more accustomed to fast, seamless digital experiences, organizations need to constantly update their solutions. Only by providing efficient and user-friendly access are organizations able to maintain high levels of user satisfaction and productivity. - Competitive advantage
In a fast-paced business environment, being able to quickly adapt and integrate advanced identity management solutions can provide a competitive edge, improving security, operational efficiency, and – more than anything else – customer trust.
Changing business requirements

As our interactions become more digital, organizations need to adapt to new ways in steady and regular intervals. Operating models need to adapt to the technology as it evolves.
- Ease of use vs. higher security
Users expect easy and quick access. This can conflict with the need for robust security measures, which is also increasingly – and rightly – a hard requirement for most users. Protection against identity fraud or theft, for example, should be as secure and seamless as showing a physical ID in real life. Balancing these requirements is a continuous challenge. - Agility and flexibility
With emerging methodologies like Agile, Lean development, and SAFe, business requirements are changing rapidly, adapting to market trends, responding to customer needs, and necessitating an update of the IT strategy. Therefore, identity management systems need to be flexible to accommodate new projects, technologies, or organizational changes. - Technological debt
Rapid technological changes – like blockchain and AI – but also paradigm shifts – like containerization and cloud adoption – are opening up a whole new world of possibilities for digital identity management. Implementing and mastering these new technologies can be a major challenge for organizations, e.g., requiring scarce subject matter experts and financial resources.
Legal requirements and compliance

Ensuring that identity management practices comply with ever increasing regulations (e.g., GDPR, FADP) involves ongoing monitoring, auditing, and reporting. Protecting user privacy and managing consent for data collection and usage requires meticulous handling of personal data.
Data privacy
One major concern with digital identity management are data privacy considerations. The revised FADP enacted on September 1, 2023, reflects modern security threats and better protects Swiss citizens’ personal data. With this revision, a number of key changes were introduced. For example, organizations must:
- provide individuals with clear information about the storage, processing, and use of the data,
- take into account the latest data security and processing principles at the planning and design stage of applications, keeping the privacy of users in mind, and
- communicate a cyberattack or a security breach to users as soon as possible to avoid legal sanctions and further complications.
By now, companies should have implemented the necessary measures, such as a data audit, privacy policy updates, enhanced security, and the introduction of a DPO.
A government-issued E-ID might bring substantial organizational relief to companies. However, according to the Federal Council’s dispatch on the upcoming e-ID Act adopted in November 2023, the E-ID won’t be offered before 2026. Until then, a number of questions still needs to be answered.
FINMA-regulated outsourcing

Given the challenges described in this section, outsourcing digital identity management seems like an appealing option. FINMA, Switzerland’s independent financial-markets regulator aiming to protect individual financial-market clients, has published a circular on the outsourcing of services. In a nutshell:
- Definition
Outsourcing […] occurs when a company mandates a service provider to perform all or part of a function that is significant to the company’s business activities. Significant functions are those that have a material effect on compliance with the aims and regulations of financial market legislation. - Requirements for outsourcing companies
- Companies must keep an inventory of outsourced functions at all times.
- The service specifications must be agreed in line with the aims of the outsourcing and documented before the agreement is signed.
- Where multiple functions are outsourced to the same service provider, the concentration of risk must be taken into account.
- The service provider must offer a guarantee of permanent service provision.
- The outsourced function must be integrated into the company’s internal control system, and a unit within the company must be named as responsible for monitoring and controlling the service provider.
- Responsibility
The company remains accountable to FINMA in the same way as it would if it performed the outsourced function itself. - Security
Where security-relevant functions are outsourced – particularly in information technology –, the company and the service provider must contractually agree security requirements. - Audit
The company, its audit firm, and FINMA must be able to verify the service provider’s compliance with supervisory regulations.
Why – or not – outsource digital identity management

As we have just seen, digital identity management comes with numerous challenges affecting all levels of an organization. For example, attackers tend to target weak «human links», high-profile breaches are likely to jeopardize operations and trust, current processes often provide a poor user experience, and fragmented global data and privacy regulation is creating compliance challenges.
Going forward, digital transformation may gain even more momentum. Therefore, companies that want to play it safe and focus on their core business may consider outsourcing digital identity management to a specialized service provider. Let us compare the «in-house» and the «outsourcing» scenarios.
The most prominent benefits of operating your own identity management system
Here’s why managing digital identities in-house may be a viable option for an organization:
- Security control
Direct oversight allows for security measures that are specifically designed to counteract known threats and vulnerabilities within the organization. In case of an incident, in-house teams can quickly respond. - Compliance and data privacy
In-house management ensures that all identity processes align with the latest global data privacy and security regulations. Plus, it reduces the risk of exposure through third-party breaches and ensures better control over data handling practices. - Seamless integration
Digital identity solutions can be customized to fit seamlessly with existing systems and processes, leading to a more cohesive and efficient IT environment. - Cost efficiency
While initial setup may be expensive, managing digital identities in-house can lead to long-term cost savings by reducing reliance on third-party services.
|
In-house identity management |
||
|
Benefits |
Risks |
|
|
Security |
Specific security measures to counteract threats |
Lack of robust security measures due to limited resources |
|
Compliance and data privacy |
Identity processes align with latest regulations |
Difficulty to keep up with evolving regulations |
|
Integration |
Customized solution to fit seamlessly with existing systems and processes |
Complex task requiring significant financial and human resources |
|
Scalability |
|
Scaling systems efficiently as company grows |
|
Costs |
Long-term cost savings by reducing reliance on third-party services |
Significant investment in technology and infrastructure may strain limited resources |
|
Expertise |
Lack of the specialized knowledge may lead to security gaps and operational inefficiencies |
|
The most prominent risks of operating your own identity management system
As usual, there is also a flipside. When running your own digital identity management, you should be aware of the following risks:
- Security vulnerabilities
Limited resources might prevent organizations from implementing robust security measures, making their systems more susceptible to cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access. - Compliance challenges
Keeping up with evolving regulations and industry standards can be difficult, increasing the risk of non-compliance and potential legal penalties. - Integration and scalability
Integrating a digital identity solution may be a complex task requiring significant financial and human resources. In addition, as a company grows, it might struggle to scale their systems efficiently, leading to performance issues and operational bottlenecks. - Financial resources
Managing digital identities requires significant investment in technology and infrastructure, which can strain the limited resources of smaller companies or is avoided by companies that consider IAM a negligible topic. - Lack of expertise
There may be a lack of the specialized knowledge required to effectively manage digital identities, leading to potential misconfigurations, security gaps, and operational inefficiencies.

The most prominent benefits of outsourcing digital identity management
Outsourcing allows companies to adopt a holistic approach to digital identity management. By teaming up with a specialized service provider, they make sure that the main challenges listed above are tackled. Not surprisingly, the benefits are similar to those in the in-house scenario, but clearly more pronounced:
- Enhanced security
A specialized service provider has the necessary technological resources and in-depth knowledge to make sure that robust security measures are in place to protect a company from ever-evolving cyberthreats and unauthorized access. Plus, an outsourced provider handles security patches and system updates at regular intervals.
Challenge «Changing business requirements» - Full compliance
Outsourcing to a provider with compliance capabilities reduces the risk of data breaches and regulatory penalties. Standard solutions are often designed with compliance and security in mind, incorporating the latest regulatory requirements and security standards.
Challenge «Legal requirements and compliance» - Streamlined integration
Standard solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure and applications, providing connectors and APIs that simplify the integration process. This reduces the effort and technical know-how required to connect disparate systems with their own requirements and protocols.
Challenge «Complexity of maintaining IDM systems» - Higher scalability and flexibility
Standard solutions are built to scale according to the needs of the business, allowing for easy adjustments as the company grows or changes. This flexibility simplifies the management of identity requirements over time.
Challenge «Changing business requirements» - Lower operational costs
Outsourcing eliminates the need for substantial upfront investments in infrastructure, software, and specialized personnel. The provider handles these aspects, converting capital expenses into predictable operational expenses and reducing overall costs.
Challenge «Resource shortages (financial)» - Easier access to expertise
Outsourcing providers specialize in identity management and bring in-depth knowledge of the latest technologies and best practices. This expertise enables quicker implementation and more effective management of identity solutions, accelerating digital transformation efforts. Internal IT teams can thus focus on strategic initiatives and core business functions.
Challenge «Resource shortages (human)» - Reduced implementation time
With standardized solutions, third-party providers can deploy identity management systems much faster than building in-house solutions. This rapid deployment allows companies to stay ahead of security threats, respond to incidents, and enhance user experience.
Challenge «Need for rapid adaptation»
|
Outsourced identity management |
||
|
Benefits |
Risks |
|
|
Security |
Technological resources and in-depth knowledge required to protect a company from ever-evolving cyberthreats |
No direct control over identity processes and data security practices |
|
Compliance and data privacy |
Reduced risk of data breaches thanks to expertise and also solutions that are «compliant by design» |
Challenge to comply with regulations in different jurisdictions |
|
Integration |
Standard solutions integrate seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure and applications |
Potentially technically complex and costly |
|
Scalability |
Built to scale according to the needs of the (growing) business |
|
|
Costs |
No need for major upfront investments in infrastructure, software, and specialized personnel |
|
|
Expertise |
Expertise enables quicker implementation and effective management of identity solutions, accelerating digital transformation efforts |
|
|
Implementation |
Rapid deployment speeding up time to benefit |
|
|
Transparency |
Potential lack of transparency regarding how identity data is managed, stored, and protected |
|
|
Customization |
If not fully customized, outsourced solution may lead to gaps in functionality and performance |
|
|
|
|
|
The most prominent risks of outsourcing digital identity management
Even though outsourcing digital identity management benefits a company on multiple levels, it is important to also be aware of the risks. The most important ones:
- Loss of direct control and security
Outsourcing identity management means relinquishing direct control over identity processes and data security practices. - Compliance and regulation
Different jurisdictions have varying data protection laws. Ensuring compliance with all relevant regulations can be challenging. Furthermore, outsourcing often involves transferring data across borders, which can raise concerns about data sovereignty and the adequacy of data protection in the provider’s jurisdiction. - Integration and system compatibility
Integrating the third-party identity management system with existing organizational systems can be technically complex and costly. - Transparency issues
There may be a lack of transparency regarding how identity data is managed, stored, and protected by the third-party provider. - Customization limitations
The outsourced solution may not fully meet the specific needs of the organization, leading to potential gaps in functionality or performance.
Operating models for digital identity systems

The level of outsourcing services can be chosen dynamically ranging from a complete do-it-yourself approach to full outsourcing.
In-house development and operations

Operating digital identity systems in-house requires defining clear objectives, selecting appropriate technologies, and establishing a robust governance framework. Proceed as follows: Assemble a skilled team, ensure seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure, implement strong security measures like MFA and encryption, and conduct regular audits for compliance. You will also need to educate users on security best practices and maintain real-time monitoring and incident response protocols. Furthermore, plan for scalability and continuously update the system to address new threats and integrate advancements.
Solution support

Organizations that choose an external identity management solution may also want to buy support services. One option is a service level agreement (SLA). It ensures a professional emergency response in case of an incident and provides comprehensive protection. Depending on the nature of the SLA and the criticality of an incident, response times and reachability vary. If desired, solution support is available 24/7, including on public holidays.
In the event of an issue, experienced engineers with specialized skills and in-depth technical knowledge of the solution used are available to help resolve complex problems. Where necessary, corrective measures are initiated.
Operations

A so-called operations model enables shared responsibility for running the solution. While the organization operates the infrastructure of the solution that runs together with the backend applications in their data center, the service provider ensures operation of the solution itself on top of the infrastructure.
This model covers maintenance of the solution itself, including patches, hot fixes, and security updates, as well as the operating system, if necessary. Thanks to predictive maintenance and monitoring, potential issues are avoided, detected at an early stage or, if they occur, solved.
«Operations» also includes topics such as documentation and regular health checks, from which recommendations for capacity management, service continuity, and vulnerability management are derived.
Managed service

The «managed service» model transfers full responsibility for operation and availability of the solution to the service provider. This option ensures a highly scalable, cloud-based SaaS solution that offers first-class performance and reliability.
In addition to the services of the «operations» model, the «managed service» model covers topics such as infrastructure, network, monitoring, backup, and recovery, plus a full life cycle and release management of the solution, including security fixes and product upgrades.
Embracing digital transformation with the right amount of support
There’s no denying it: Digital identities are a core element of your company’s DNA.
For those who want to master or speed up digital transformation, the key is to thoroughly manage and protect digital identities on all levels. This will not only help you to enhance cybersecurity, but also to strengthen customer trust and meet regulatory requirements.
Should your resources be limited or should you be unfamiliar with the topic, outsourcing digital identity management can be a viable option. Analyze your business, technical, and operational requirements and choose a solution that exactly meets your needs.
Delegating digital identity management to a trusted partner will give you peace of mind and free up time, allowing you to focus on the things that truly matter to your organization.