- On this page
- What is Vulnerability Management?
- Common Types of Vulnerabilities
- Fortifying Your Defenses: Key Mitigation Strategies
- The Importance of Vulnerability Management
- Steps in the Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
- Benefits of Effective Vulnerability Management
- Data Compliance
- Navigating Regulatory Landscape with Vulnerability Management
- FAQs about Vulnerability Management
Any company concerned with cybercrime, legal difficulty, and reputational harm would do well to seek out security solutions that improve cybersecurity and ensure legal compliance. Vulnerability management is one of such critical areas of focus to meet data protection regulations and reduce cybersecurity risks in an organization’s IT environment. This article will discuss vulnerability management's role inside an organization and how vulnerability management can help organizations achieve data compliance.
What is Vulnerability Management?
Vulnerability management refers to the ongoing process of identifying, evaluating, and mitigating security weaknesses within an organization’s information security management systems (ISMS). This proactive approach ensures that IT systems remain protected from cyberattacks and data breaches by continuously monitoring for vulnerabilities across software, hardware, and networks. By addressing these potential risks before they are exploited, organizations can maintain a more resilient security posture and meet compliance requirements.
What are Vulnerabilities
Common Types of Vulnerabilities
.png?width=864&height=484&name=2023%20website%20blog%20banners%20(800%20%C3%97%20350%20px).png)
- Network vulnerabilities: a gap that might be exploited by an attacker to gain unauthorized access to a system; could be caused by a bug in software, hardware, or administrative procedures.
- Operating system vulnerabilities: a weakness in the operating system that hackers may use to get access to a system.
- Configuration vulnerabilities: this includes incomplete installs, poorly conducted system upgrades or updates, and default deployments that can facilitate hackers’ attempts to exploit and attack networks and devices.
- Application vulnerabilities: This is a system loophole in an application that could be used to breach the application's security.
Fortifying Your Defenses: Key Mitigation Strategies
- Vulnerability scanning - detection, evaluation, and reporting of security flaws.
- Vulnerability assessment - delivering information for cybersecurity threat mitigation and prevention.
- Vulnerability remediation - discovering, fixing, and neutralizing IT security issues in an organization.
The Importance of Vulnerability Management
In today's digital landscape, vulnerability management is critical due to the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats. According to research by Ponemon Institute, 60% of breaches in 2019 resulted from known vulnerabilities that had not been patched1. With the rising costs of cybercrime, which are projected to reach $10.5 trillion by 2025 2, businesses face substantial financial and reputational risks if vulnerabilities are not adequately managed.
As businesses scale their cloud solutions and introduce new applications, their information security management systems (ISMS) must handle a wider attack surface. Without a systematic approach to identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, hackers can exploit weaknesses, resulting in potentially devastating breaches. Effective vulnerability management ensures that businesses can swiftly address threats, safeguarding critical resources and meeting regulatory standards such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and NIST.
Steps in the Vulnerability Management Lifecycle
1. Asset Discovery and Inventory
- Identify all IT assets, including software, hardware, and network devices, within the organization.
- Create a comprehensive inventory for accurate risk assessment.
2. Vulnerability Assesment and Scanning
- Use automated tools to scan systems for known vulnerabilities.
- Conduct manual assessments to identify potential weaknesses not detected by automated tools.
3. Vulnerability Prioritization
- Assess the severity and potential impact of each identified vulnerability.
- Prioritize vulnerabilities based on factors like exploitability, impact, and business criticality.
4. Patch Management
- Apply security patches and updates promptly to address vulnerabilities.
- Test patches in a controlled environment to minimize the risk of unintended consequences.
5. Configuration Management
- Enforce security best practices through configuration hardening.
- Implement secure default configurations to reduce attack surfaces.
6. Remediation and Mitigation
- Address vulnerabilities through a combination of patching, configuration changes, and other mitigation techniques.
- Implement compensating controls to mitigate risks for vulnerabilities that cannot be immediately addressed.
7. Verification and Validation
- Conduct post-remediation scans to confirm that vulnerabilities have been successfully addressed.
- Validate the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
8. Continuous Monitoring
- Maintain ongoing monitoring of systems and networks to detect new vulnerabilities.
- Implement a proactive threat intelligence program to stay informed about emerging threats.
9. Reporting and Documentation
- Generate regular reports on vulnerability status, remediation efforts, and overall security posture.
- Maintain detailed documentation for compliance and auditing purposes.
Benefits of Effective Vulnerability Management
1. Reduced Security Risks
A robust vulnerability management program significantly lowers the risk of cyberattacks by identifying and addressing weaknesses before they can be exploited.
2. Compliance with Regulations
By implementing vulnerability management, organizations can meet the security requirements of industry regulations like HIPAA and PCI DSS, avoiding potential penalties.
3. Improved Operational Efficiency
Automating vulnerability scanning and remediation processes reduces manual work, allowing IT teams to focus on other critical tasks, leading to better overall performance.
4. Enhanced Reputation and Customer Trust
By consistently managing vulnerabilities, businesses demonstrate a strong commitment to security, enhancing their reputation and fostering trust with clients and partners.
Challenges of Vulnerability Management
1. Evolving Threat Landscape
New vulnerabilities and attack techniques emerge constantly, making it difficult to stay ahead of threats. Zero-day vulnerabilities, which are unknown to security vendors, pose significant risks.
2. Resource Constraints
Limited budgets, staffing shortages, and competing priorities can hinder effective vulnerability management. Small and medium-sized businesses may have particular challenges in allocating sufficient resources to security.
3. Complex IT Environments
Large and diverse IT infrastructures can make vulnerability assessment and remediation complex. Interconnected systems and dependencies can amplify the impact of vulnerabilities.
4. False Positive and False Negative Alerts
Vulnerability scanning tools may generate false positive alerts, wasting time and resources. Conversely, false negative alerts can leave critical vulnerabilities undetected.
5. Lack of Skilled Personnel
A shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals can limit an organization's ability to implement effective vulnerability management practices. Hiring and retaining qualified staff can be challenging and costly.
6. Third-Party Risk Management
Relying on third-party vendors introduces additional risk, as vulnerabilities in their products or services can impact the organization. Ensuring that third parties maintain adequate security standards can be difficult.
7. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Adhering to industry regulations and compliance standards can add complexity to vulnerability management. Staying up-to-date with evolving regulations can be time-consuming.
By understanding these challenges and implementing effective strategies to address them, organizations can improve their security posture and mitigate the risks associated with vulnerabilities.
Best Practices for Vulnerability Management
1. Regular Vulnerability Scanning
Conduct regular vulnerability assessments to ensure that your systems are continuously monitored for new threats and weaknesses.
2. Prioritize Based on Risk
Focus remediation efforts on the vulnerabilities that pose the highest risk to your organization. This includes assessing potential impacts and exploitability.
3. Patch Management
Ensure that patches and updates are applied promptly to address vulnerabilities in software and hardware systems.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Reporting
Maintain a consistent monitoring process to detect and manage vulnerabilities in real time. Comprehensive reporting helps track trends and make data-driven decisions.
Data Compliance
The term "data compliance" is used to describe the observance of laws and guidelines that require an organization to take precautions against the loss, theft, and abuse of the private data it stores and processes.
There are several shapes that these regulations might take. Whether they are industry standards, federal or state laws, or supranational regulations like GDPR, regulations governing the handling of personal information will often detail the categories of data that must be safeguarded, the forms of processing that are permitted, and the consequences for businesses that do not comply.
These regulations are essential to ensuring the privacy, security, and veracity of customers’ data. By adhering to these rules, businesses may avoid costly fines and maintain the trust of their customers.
Learn more: Conquering Governance and Compliance Challenges
Investing in effective cybersecurity and data protection solutions is thus crucial for organizations to meet compliance and protect their sensitive data. Appropriate data security solutions also allow businesses to boost their cybersecurity hygiene and operational efficiency.
Navigating Regulatory Landscape with Vulnerability Management
Inadequate cybersecurity practices and the importance of data privacy and protection among digital businesses are eliciting a growing reaction from regulators. An unpatched software flaw can be a major factor that provides an entry point for attackers to get access to sensitive data or systems.
Vulnerability management methods are thus mandated by several regulatory and governance frameworks for achieving compliance with regulations including PCI DSS, HIPAA, NIST, ISO 27001, SOC2, FISMA, NYDFS, CMMC, and GLBA. Organizations that accept credit card payments, for instance, are subject to strict regulations from the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), one of which is to do frequent vulnerability scans and penetration testing to uncover security flaws in their systems. Thus, it is recommended that businesses employ vulnerability management solutions for the features that may help them meet compliance requirements.
Vulnerability management solutions can do continuous vulnerability assessments and remediation, avoiding the risks associated with either ignoring them or failing to find them. Once a threat is detected and prioritized, mitigation efforts are put into place. These remediation actions and the security audit feature of vulnerability management are essential practices to enable organizations to meet the level of data protection required by internal and external regulations.
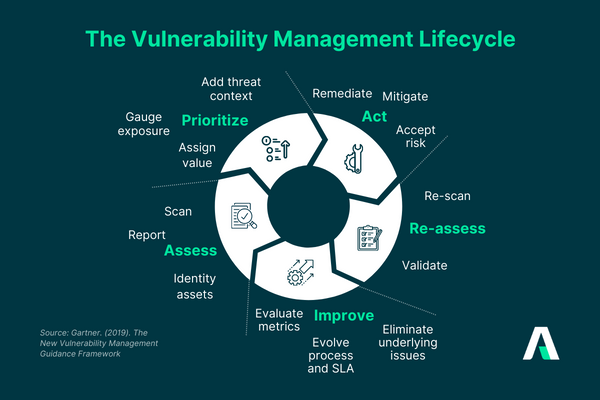
With a cyclical approach to vulnerability management, organizations can minimize the life span of vulnerabilities and non-compliance gaps in their systems. Hence, vulnerability management can proactively fortify an organization’s security posture and maintain compliance, reducing the risk of data breaches and associated costs.
Vulnerability management’s important goal is to reduce the risk of being exploited through the four most common types of vulnerabilities. Contact Adnovum to implement a proactive vulnerability management approach that effectively protects your organization’s IT infrastructure and meets compliance requirements.
FAQs about Vulnerability Management
1. What is vulnerability management, and why is it important for businesses?
Vulnerability management is the process of identifying, evaluating, and addressing security weaknesses in IT systems. It is crucial for protecting organizations from cyber threats and ensuring compliance with industry regulations like HIPAA and PCI DSS.
2. How do vulnerability management and information security management systems (ISMS) work together?
Information security management systems (ISMS) provide the framework for securing an organization's data and resources. Vulnerability management is an integral part of ISMS, focusing on identifying and mitigating risks within this framework.
3. How often should vulnerability management be performed?
Vulnerability management should be an ongoing process, with regular assessments and continuous monitoring to address new risks as they arise. The frequency depends on the complexity of the IT environment and the level of risk exposure.
References:
1. Ponemon. (2020). Costs and Consequences of Gaps in Vulnerability Response.
2. Cybersecurity Ventures. (2022). 2022 Official Cybercrime Report.
3. IBM and the Ponemon Institute. (2022). Cost of a Data Breach 2022
4. Ponemon Institute and Servicenow. (2020). Costs and Consequences of Gaps in Vulnerability Response